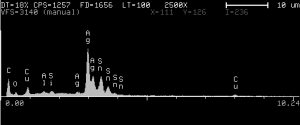
EDS, EDX or EDAX Analysis
Energy dispersive X-ray analysis, also known as EDS analysis, is a technique used to identify the elemental composition of a sample or small area of interest on the sample. During EDS a sample is exposed to an electron beam inside a scanning electron microscope (SEM). These electrons collide with the electrons within the sample, causing some of them to be knocked out of their orbits. The vacated positions are filled by higher energy electrons which emit x-rays in the process. By analyzing the emitted x-rays, the elemental composition of the sample can be determined. EDS is a powerful tool for microanalysis of elemental constituents.
EDS analysis is usually a destructive technique due to cutting the sample to size to fit into the chamber.
EDS can also be referred to as EDX or EDAX analysis.
EDS analysis is useful in identifying certain types of polymeric materials as shown here: EDS Analysis of Polymers.
For organic materials analysis and/or identification, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy or FTIR is more suitable. More information about FTIR can be found on our FTIR analysis page.
SEM/EDS Analysis of Alloy Plating
SEM Lab, Inc. supports routine quality control testing of alloy plating using SEM/EDS analysis to verify composition. Some examples include zinc-nickel alloy, electroless nickel-phosphorous alloy, tin-lead alloy, and a wide range of other alloy combinations. More details on this service can be found here.
QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
An EDS spectrum can give information about the elements in a sample as well as their quantities.
EDS IS BEST SUITED FOR:
- Metals and metal alloys
- Ceramics
- Minerals