Failure Analysis of Film Capacitors
Failure Analysis of film capacitors usually involves corrosion to the metallized film, electrical overstress, solder stresses or mechanical damage.
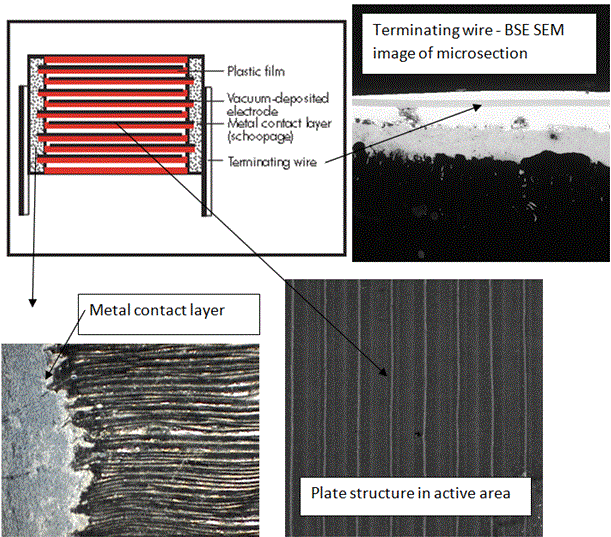
Film capacitors use stacked metallized polymer films to form the capacitor structure. The metal plates are usually evaporated aluminum. The polymers can be Polyethylene-terephthalate (PET), polycarbonate (PC), polypropylene (PP) and others. The internal structure of these capacitors is illustrated here.
Film capacitors can fail due to the following:
- Corrosion damage to the metallized film
- Electrical overstress
- Solder stresses
- Mechanical damage
The metallization on the film is made thicker to support termination to the metal contact layer (see next image). The relative peak heights for aluminum (Al-Ka1) and carbon (C-Ka1) are a measure of the aluminum thickness..